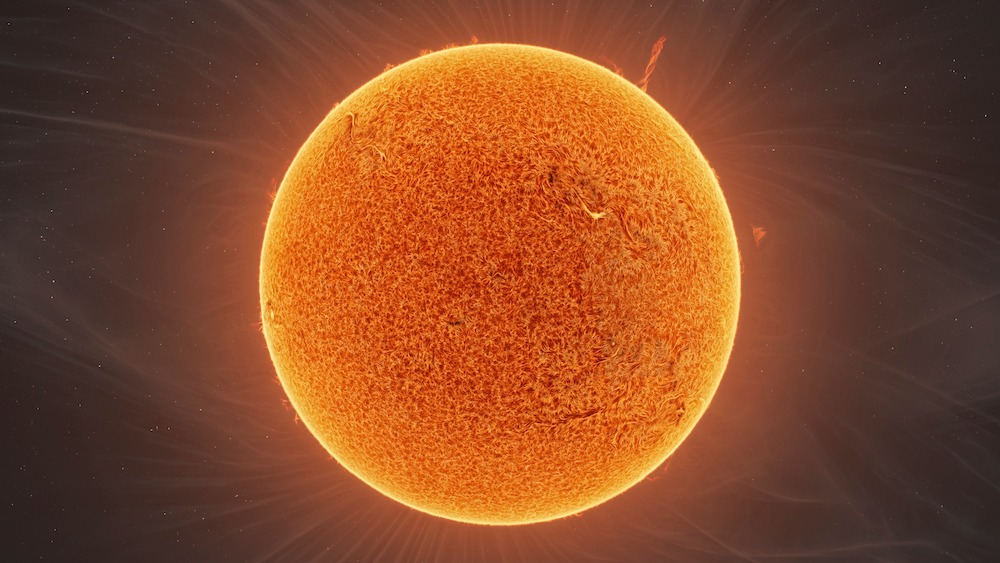
The Sun, the fiery orb at the center of our solar system, is more than just a source of light and warmth. It’s a complex celestial body that powers life on Earth and has captivated human imagination for millennia.
A Nuclear Powerhouse
At its core, the Sun is a massive nuclear reactor. Hydrogen atoms fuse together under immense pressure and temperature to create helium. This process, known as nuclear fusion, releases an enormous amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This energy is what sustains life on Earth.
Structure and Layers
The Sun is composed of several layers:
- Core: The innermost layer where nuclear fusion takes place.
- Radiative zone: Energy from the core is transported outward through radiation.
- Convective zone: Energy is transported by convection currents, similar to boiling water.
- Photosphere: The visible surface of the Sun, where sunspots and solar flares occur.
- Chromosphere: The thin layer above the photosphere, often seen as a reddish glow during eclipses.
- Corona: The outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, extending millions of miles into space.
Solar Activity
The Sun is not a static object. It exhibits various forms of activity, including:
- Sunspots: Dark, cooler regions on the Sun’s surface caused by magnetic activity.
- Solar flares: Sudden bursts of energy released from the Sun’s surface.
- Coronal mass ejections (CMEs): Large clouds of plasma ejected from the Sun’s corona.
Solar activity can have significant impacts on Earth, such as disrupting communication systems and power grids. However, it also plays a vital role in the Earth’s climate and atmosphere.
The Sun’s Future
While the Sun is a relatively stable star, it will eventually exhaust its hydrogen fuel and begin to evolve. In billions of years, it will become a red giant, engulfing the inner planets. Eventually, it will shed its outer layers, leaving behind a dense core known as a white dwarf.
The Sun is a remarkable celestial object that has shaped the history of our planet and continues to fascinate scientists and the public alike. As we continue to explore and study the Sun, we gain a deeper understanding of our place in the universe.